Hepatitis C
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection. It affects the liver and causes inflammation of the liver, known as hepatitis. Over time, it can lead to serious liver damage, liver hardening and liver cancer.
It is spread primarily through contaminated blood and needles.
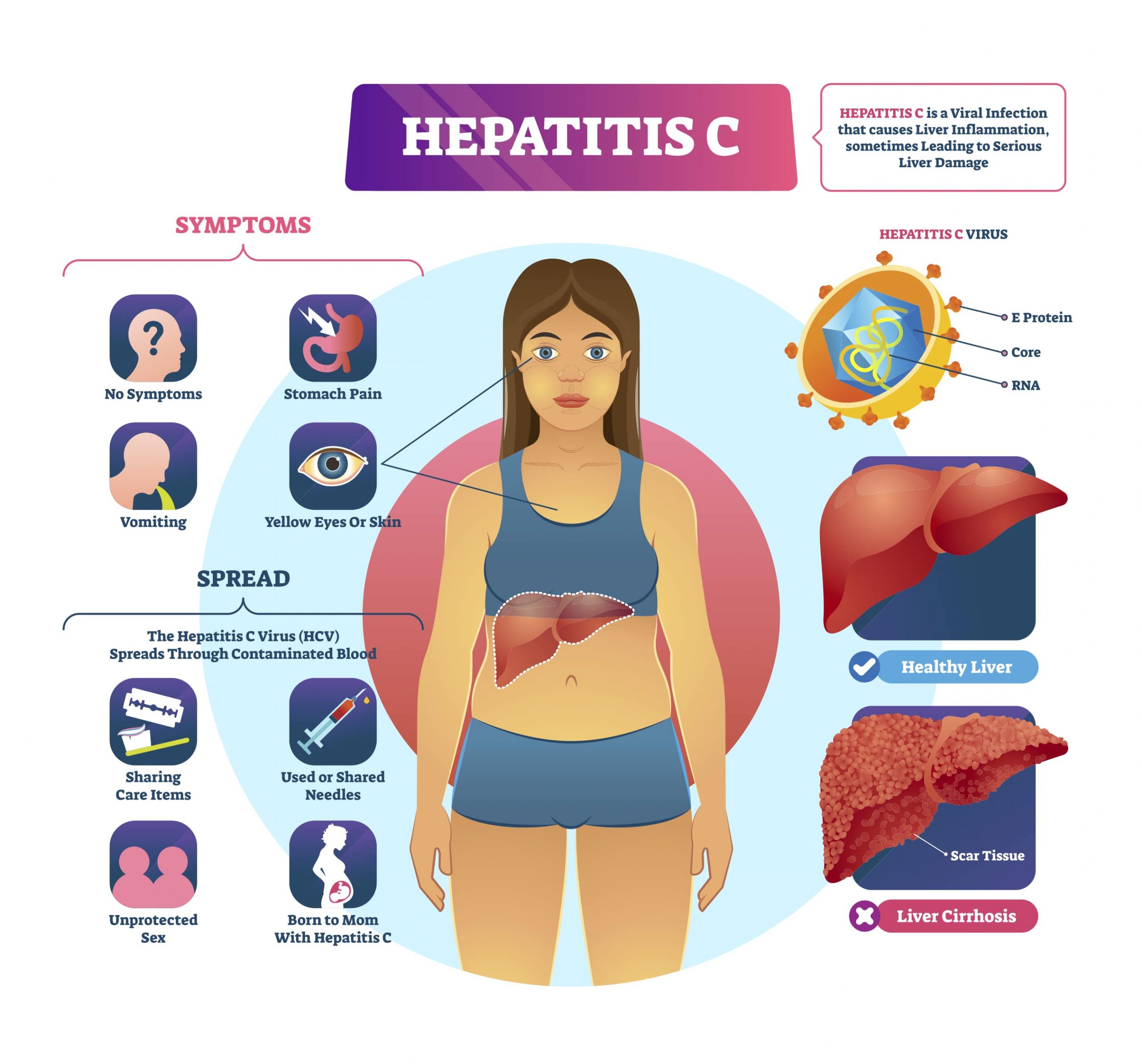
Most people with hepatitis C do not have symptoms for many years until the virus damages the liver enough to cause signs and symptoms of liver disease.
Signs and symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Poor appetite and nausea
- Jaundice (yellow discolouration of the skin)
- Dark-coloured urine
- Fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
- Confusion, drowsiness (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Spiderlike rash (spider naevi)
- Bruises
Rarely, hepatitis C can also cause weight loss, skin rash and joint pains.
All patient with hepatitis C needs treatment to prevent future complications and to prevent transmitting it to other people. They should see a specialist for proper treatment.
Hepatitis C is caused by a virus called hepatitis C virus. It is an RNA virus that is transmitted through contact with contaminated blood products and needles. It is commonly transmitted amongst IV drug abusers when they share needles. An outbreak of hepatitis C also occurred when blood products contaminated with the virus are used for patients.
Risk factors for hepatitis C includes:
- Blood transfusion before 1992, blood products for clotting problems before 1987
- Use of needles to take illegal drugs, especially if the needles are shared
- Snort cocaine
- Healthcare workers who work around blood or needles
- Dialysis patients
- Close daily contact with a person infected with hepatitis C
- Have body piercings or tattoos
- Been in prison
- Born to a mother with hepatitis C
Whoever who have the above risk factors should screen for the presence of hepatitis C.
Diagnosis of hepatitis C is done through a blood test. A screening blood test can be false positive and confirmatory testing is needed.
Treatment of hepatitis C uses direct-acting antiviral (DAA) tablets. They are safe and effective. The tablets are taken for 8 to 12 weeks and will result in a cure for more than 95%. The medication is expensive in most countries.




