Oesophageal Motility Conditions
What is Oesophageal Motility Conditions?
Oesophageal motility disorders refer to conditions where there is no structural issue with the swallowing tube, the oesophagus, but there is a problem with the movement of food in the oesophagus. This could be a problem due to the lining, muscles or nerves of the oesophagus. These conditions are not uncommon but are unfortunately often misdiagnosed as reflux, with a failure of response to treatment.
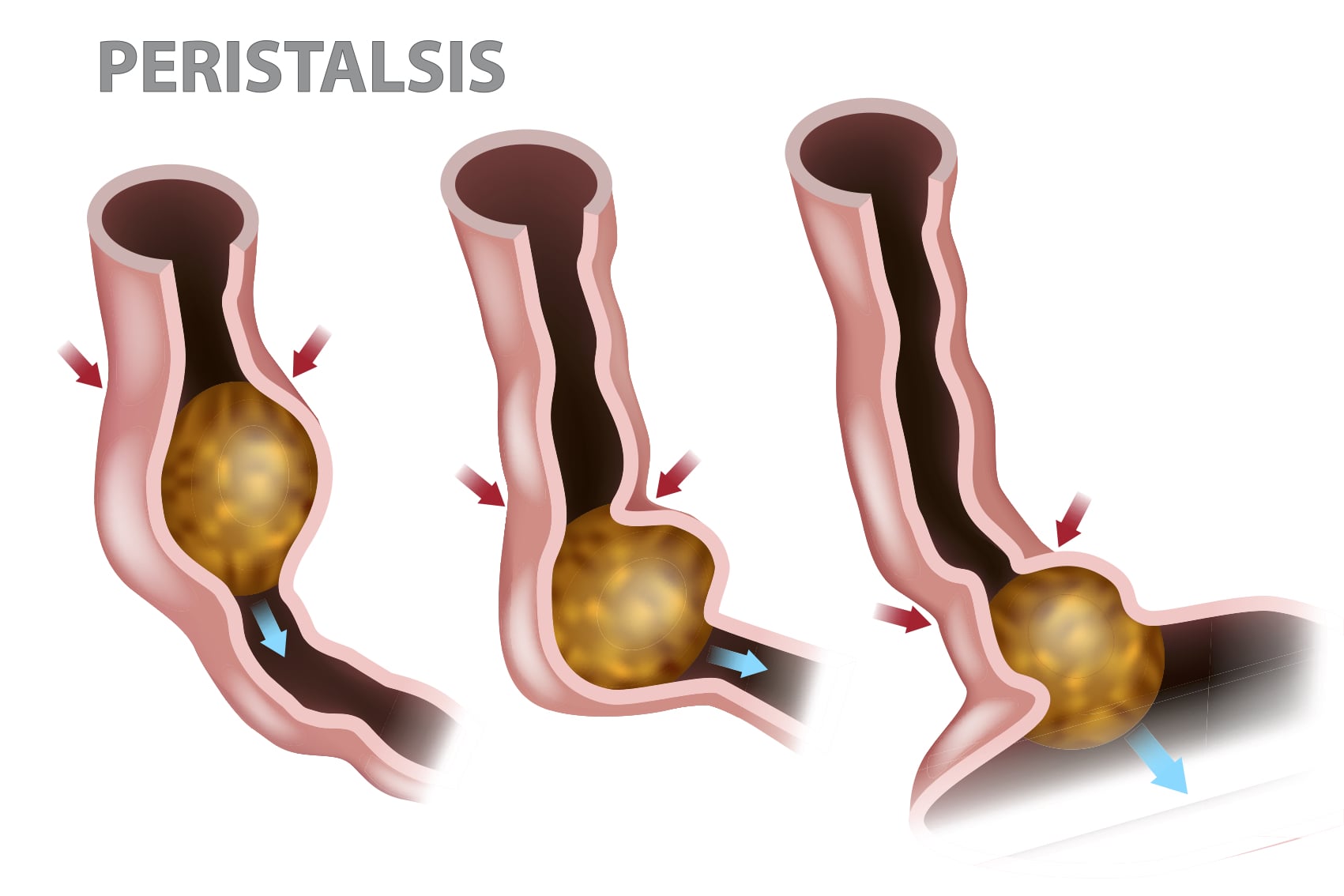
Symptoms can be variable, and can include:
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Chest pain (unrelated to heart disorders)
- Choking with episodic breathlessness
- Regurgitation and unexplained vomiting
If you have any of the symptoms described above, that persists despite over the counter medications. These disorders are often misdiagnosed, and a special test beyond an endoscopy may be necessary to secure a diagnosis. Your doctor will be the best person to advise.
Oesophageal motility disorders are classified according to an International Guideline known as the Chicago Classification.The problem can be either one or a combination of disorders relating to the muscles that push the food down the oesophagus, to the nerves that control them. The underlying causes can be complex, ranging from viral infections to genetic variations.
There are no specific known risk factors, though a team of medical researchers are working to identify at risk individuals.
Oesophageal manometry is a motility (movement) study of your oesophagus (or food pipe), which is a long muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. The lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS) lies at the lower end of the oesophagus which meets the stomach and helps to prevent stomach contents like acid from backing up into the food pipe (referred to as acid reflux).
This test can be instrumental in diagnosing certain health conditions or disorders that are related to the oesophagus, such as achalasia, scleroderma or diffuse oesophageal spasm. It can also be conducted prior to surgery for reflux disorders and in evaluations of patients with chest pain not associated with heart disease.
The purpose of this test is to check if the muscles and nerves in your oesophagus are working well and measure the muscle contractions that occur in the oesophagus when you swallow. It also measures the coordination or force of your oesophageal muscles that move food along into the stomach. Overall, it helps to evaluate how well your oesophagus is performing.
Treatment depends on the disorder being clearly identified and defined. Treatment can include:
- Medication
- Endoscopy to dilate tight valve at the bottom of the oesophagus, using a balloon passed down an endoscope
- Surgery, also known as a myotomy
- A special hybrid surgical and endoscopic procedure is known as POEMS




