Anal Abscess and Fistula
What is Anal Abscess and Fistula?
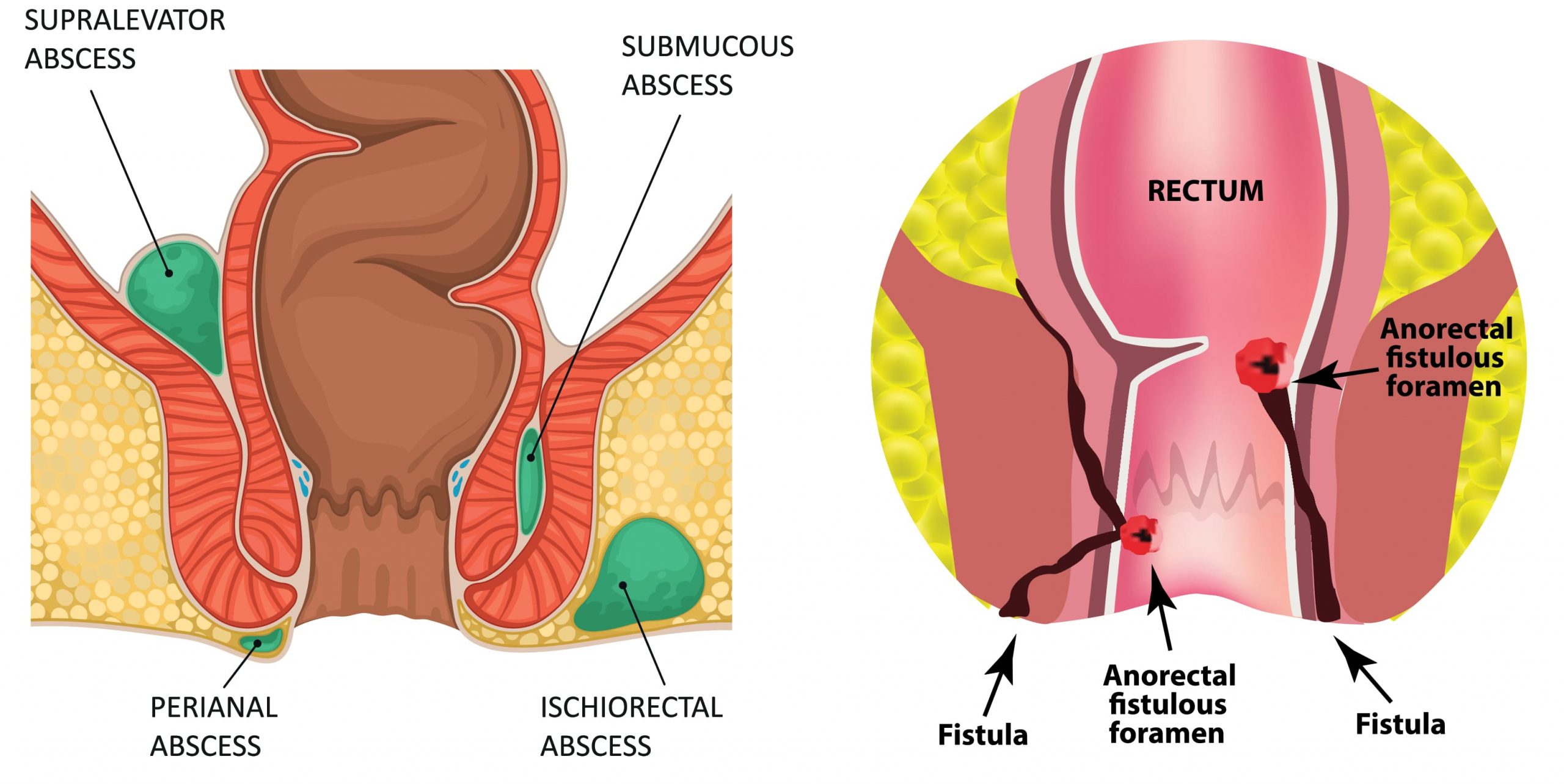
An anal abscess is an infected cavity filled with pus near the anal canal. It is usually infected by bacteria and results in pain and swelling. Patient will notice a painful lump near the anus.
An anal fistula is an abnormal tunnel that connects the anal canal to the outside skin. From the exterior, it looks like a hole near anus that exudes pus-like material, blood or stool.
Common symptoms of anal abscess and fistula include pain, swelling, redness of skin around the anus. Sometimes there is fever, bleeding and difficulty passing urine.
Patients with fistula will have some drainage from the skin of either pus, blood or fecal material. This may occur intermittently.
Anal abscess and anal fistula do not get well on their own and all patients should see a doctor for proper assessment. This should not be delayed. The doctor will take a careful history followed by a gentle examination to make a diagnosis. Occasionally ultrasound, CT scan and pelvic MRI may be needed.
Most abscess is a result of acute infection of the internal glands of the anus. Sometimes fecal material, hair or foreign material can clog an anal gland and cause an abscess. Anal fistula is often the result of a previous or current anal abscess. Fistula can sometimes be caused by inflammatory bowel disease.
RISK FACTORS for anal abscess and fistula includes diabetes, Crohn’s disease, immunosuppressive drugs, sexually transmitted diseases and anal sex.
Diagnosis of anal fissure is base of the patient’s symptoms and inspection of the anal region. Sometimes digital rectal examination may be needed. This is an examination where the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into your anus. Sometimes the examination may need to be done under general anesthesia. In some instances, ultrasound, CT scan or MRI may be needed to evaluate the abscess or fistula.
Most abscess and fistula require surgery. In some cases, the patient may need to be admitted to hospital for treatment.




