Fundamentals Of Ulcerative Colitis: Symptoms & Treatments
Ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), causes chronic inflammation of the colon’s lining is inflamed, causing ulcers to form.
Ulcerative colitis can be a draining affair, both physically and mentally. There is no known cure, and the disease can sometimes result in life-threatening and severe complications.
Ulcerative colitis symptoms
Depending on how severe the inflammation is and where they occur, the symptoms associated with ulcerative colitis may vary. In general, they may include:
- Diarrhoea, often with pus or blood
- Rectal urgency
- Rectal pain
- Stomach cramps and pain
- Joint pain and swelling
- Eye redness and pain
- Skin rash
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Lack of energy
- Growth impairment in children
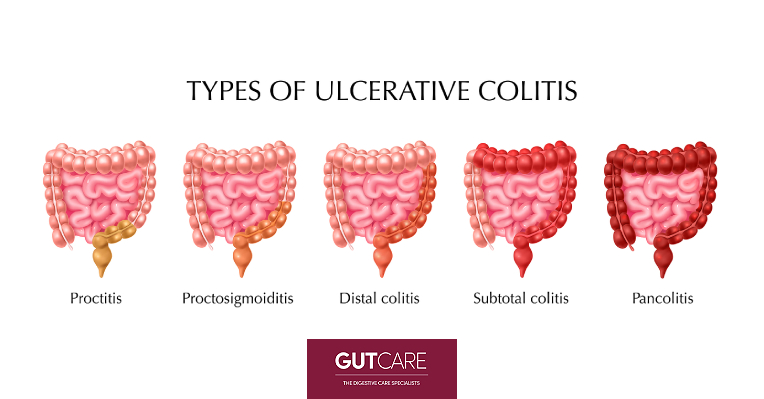
Types of ulcerative colitis
Healthcare providers classify ulcerative colitis according to the extent of inflammation found in the colon.
- Ulcerative proctitis: Often affecting the anus and the immediate surrounding area, ulcerative proctitis causes rectal urgency and bleeding.
- Proctosigmoiditis: Often affecting the sigmoid colon (lower end portion of the colon) and rectum, proctosigmoiditis causes bloody diarrhoea, stomach pain and cramps, and an uncomfortable feeling that you need to pass stools, even though your bowels are already empty, also known as tenesmus.
- Distal/Left-sided colitis: Often affecting the rectum, sigmoid, and left-side of the colon, distal/left-sided colitis causes bloody diarrhoea, stomach pain and cramps on the left side, rectal urgency and tenesmus.
- Extended/Pan–colitis: Affecting the entire colon, pancolitis causes bloody diarrhoea, stomach pain and generalised abdominal pain and cramps, rectal urgency and tenesmus.
When to visit the doctor
You should consult a gastroenterologist urgently visit if you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms. While ulcerative colitis is not a deadly disease, it can result in discomfort, pain as well as leads to further complications, which are then life-threatening.
What causes ulcerative colitis
While the exact cause of ulcerative colitis is not certain, researchers have found that stress and diet may precipitate the development of the disease. One such reason is that poor diet and stress-management may lead to a breakdown in the immune system which may result in the body attacking itself. Additionally, patients with ulcerative colitis often have family members with the same disease.
Complications of ulcerative colitis
Possible complications associated with ulcerative colitis that may be life-threatening are:
- Perforated colon, also known as a hole in the colon
- Toxic megacolon, also known as the rapid swelling of the colon
- Excessive bleeding
- Inflammation in the eyes, joints, and skin
- Increased risk of developing blood clots in arteries and veins
- Increased risk of developing colon cancer
Available treatments for ulcerative colitis
In order to assess the best treatment, your doctor or gastroenterologist may run a series of tests that includes blood tests, stool tests, colonoscopy, and CT scans. While there is currently no cure for ulcerative colitis, there are many effective treatments, such as drug therapies and surgical procedures, which can help alleviate symptoms and, in some cases, help bring the disease to a state of sustained remission.
Some of the medication therapy include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications: This is usually the first choice of treatment and works best with most individuals with the disease. An example of anti-inflammatory drugs include 5-aminosalicylates (oral tablets, enemas and suppositories).
- Immune system suppressants: They help to reduce inflammation by suppressing the immune system response that causes inflammation. Some examples include azathioprine, calcineurin-inhibitors, biologics and small molecules.
In cases of severe ulcerative colitis not responding to medication, doctors may recommend colectomy, which involves removing part of or the entire colon and rectum. Examples of surgery that you might go through are:
- Proctocolectomy: This surgical procedure involves removal of the entire colon and rectum. After this procedure, patients do not run the risk of getting rectum or colon cancer in the future. The end of the ileum (the lowest part of the small intestine) is then brought through an opening in the belly (abdominal wall) to form an ileostomy, usually on the lower right side of the abdomen. Intestinal waste passes out of the ileostomy and is collected in a specialised bag system which is placed over the opening.
- Ileoanal pouch procedure: This procedure is often done in conjunction with a proctocolectomy. After the entire colon and rectum is removed, the small bowel can be repurposed to form a small pouch, acting as a “new rectum” In rare cases, the small pouch may fail to function, resulting in its removal. In that case, the patient will end up with a permanent ileostomy.
Conclusion
Ulcerative colitis can be a serious disease and it can lead to severe complications. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should visit to your doctor early.
GUTCARE is a digestive care specialist, which means we specialise in everything related to your gut and digestive health, and that includes ulcerative colitis. Our team of experienced gastroenterologists can help you assess your situation should you experience any of the symptoms.
Click here to make an appointment with us today!
References:

HAVE AN ENQUIRY?
You may also send in an enquiry via our online form if you have questions pertaining to your visit or consultation.

FIND OUT MORE ABOUT OUR DOCTORS
Unsure of which doctor to speak to? Take a look at our doctors’ profile to find out more.




